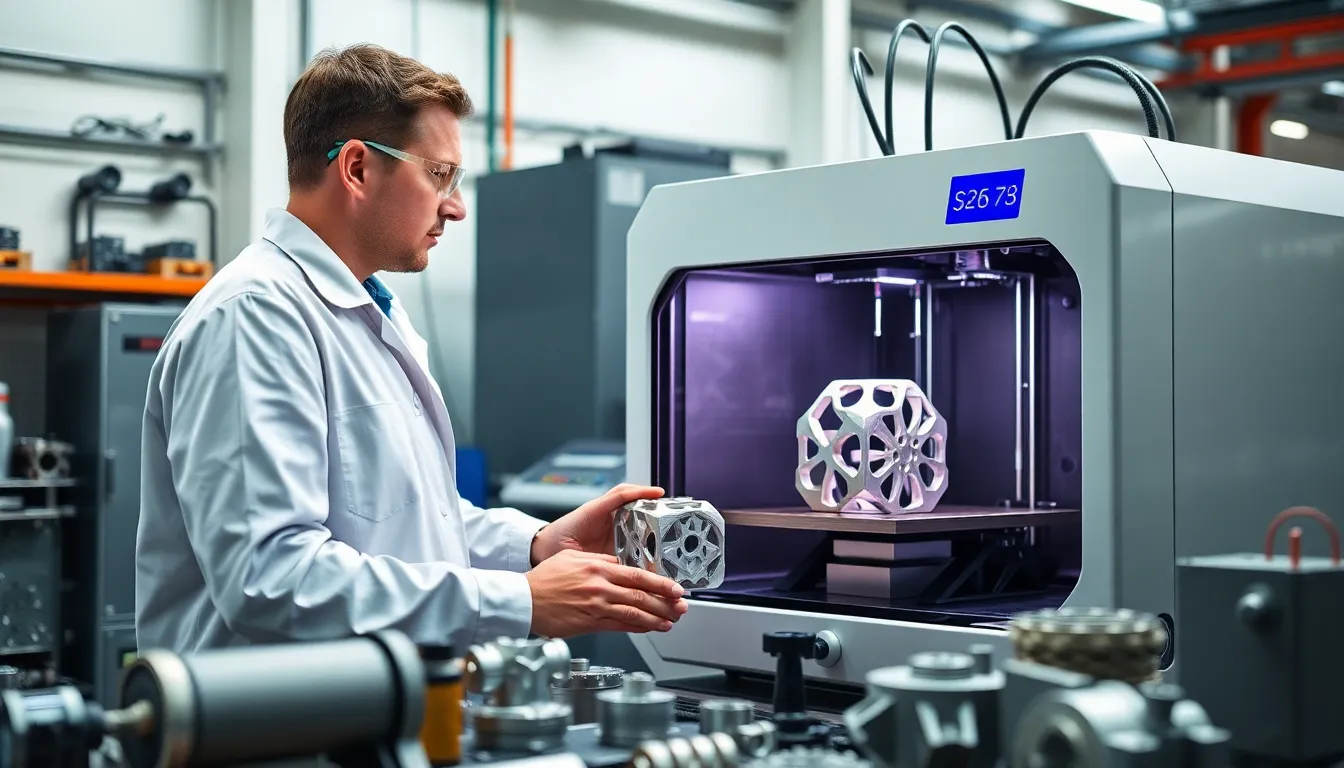
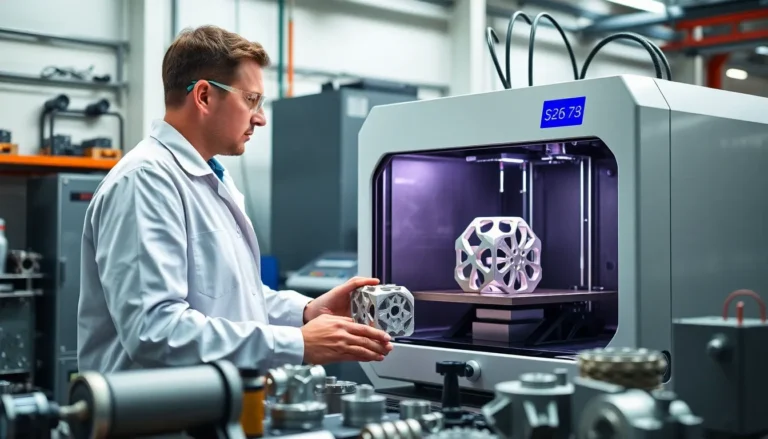
In a world where everything can be printed—yes, even your breakfast—3D printing aluminum stands out as the superhero of manufacturing. Why settle for ordinary when you can create lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant parts with a click of a button? This technology isn’t just for tech wizards; it’s transforming industries and making engineers’ dreams come true, one layer at a time.
Imagine crafting complex designs that would make even the most seasoned metalworker raise an eyebrow. From aerospace to automotive, 3D printing aluminum is revolutionizing how products are made. So buckle up as we dive into this fascinating realm where creativity meets innovation, and discover how this game-changing process can elevate projects to new heights—without the need for a magic wand.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of 3D Printing Aluminum
3D printing aluminum employs various additive manufacturing techniques that revolutionize part production. This method enables seamless integration of detailed designs and geometry that traditional machining struggles to achieve. Lightweight properties of aluminum make it a favorable choice for applications where reducing mass is critical.
Additive processes such as Selective Laser Melting (SLM) and Electron Beam Melting (EBM) play crucial roles in 3D printing aluminum. SLM utilizes high-powered lasers to melt aluminum powder layer by layer, creating components with high density. EBM, on the other hand, leverages an electron beam in a vacuum chamber, producing parts that often require minimal post-processing.
Industries increasingly adopt 3D printed aluminum components for their unique advantages. Aerospace businesses rely on its ability to produce complex structures with reduced weight and enhanced performance. Automotive manufacturers leverage this technology to streamline prototyping and create intricate parts that meet precision standards.
Durability of 3D printed aluminum is notable, as it resists corrosion and can withstand extreme conditions. Heat resistance further adds to its appeal, especially in engine components and high-temperature applications. Access to rapid prototyping accelerates product development cycles, empowering companies to bring innovations to market faster.
Utilizing this advanced technology fosters sustainability in manufacturing processes. Waste reduction occurs with additive methods, as material is only used where needed. Moreover, local production capabilities can minimize transportation costs and carbon footprints. Through 3D printing aluminum, industries are poised to enhance efficiency while adapting to modern demands for flexible manufacturing solutions.
Benefits of 3D Printing Aluminum
3D printing aluminum offers numerous advantages that positively impact manufacturing processes across various industries. This technology not only enhances performance but also promotes efficiency and sustainability in production.
Lightweight and Strong
Lightweight components contribute significantly to applications where weight reduction is crucial. Aluminum exhibits a high strength-to-weight ratio, allowing manufacturers to create strong yet lightweight parts. In the aerospace sector, reduced weight translates to improved fuel efficiency. Stronger pieces lead to enhanced performance in automotive designs, enabling vehicles to accelerate and maneuver more effectively. Additionally, complex geometries achievable through 3D printing further optimize the balance of strength and weight, making aluminum components versatile for various applications.
Cost Efficiency
Cost efficiency plays a vital role in manufacturing decisions. 3D printing aluminum minimizes material waste during production, generating only what’s necessary. This approach often reduces costs related to material usage and disposal. Rapid prototyping capabilities lower development expenses by allowing quick iterations on designs, which shortens lead times. In industries like aerospace and automotive, the savings from enhanced production processes can lead to significant overall reductions in project costs. Moreover, localized production reduces logistical expenses associated with long-distance transportation of raw materials.
Applications of 3D Printing Aluminum
3D printing aluminum finds applications across various industries due to its lightweight and durable characteristics.
Aerospace Industry
Aerospace manufacturers leverage 3D printing aluminum for parts requiring strength while minimizing weight. Turbine blades, brackets, and support structures often emerge from this technology. Designing complex geometries is essential for optimizing airflow and reducing drag. The ability to create customized components enhances performance and efficiency. Major aerospace companies increasingly adopt this fabrication method for rapid prototyping, which accelerates development timelines. Notably, the reduction in material waste contributes to sustainable practices, aligning with industry standards for environmental responsibility.
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector embraces 3D printing aluminum for creating lightweight components that improve fuel efficiency. Alloy wheels and engine components benefit from the strength and low weight this technology provides. Customization capabilities allow manufacturers to meet specific performance and design requirements effectively. By utilizing additive manufacturing, automotive companies can reduce production costs and decrease time to market. Additionally, the method supports the production of complex designs that traditional techniques often find challenging. This innovation thereby enhances vehicle performance, safety, and aesthetics while facilitating innovative designs.
Medical Field
In the medical field, 3D printing aluminum serves a unique purpose, particularly in producing orthopedic implants and surgical instruments. Custom-fit implants designed through this technology provide enhanced comfort and functionality for patients. Reducing manufacturing times accelerates the availability of critical tools and implants. High-strength aluminum meets the rigorous sterilization standards required in medical applications. Furthermore, this technology allows for rapid prototyping of medical devices, facilitating quicker adjustments based on clinical feedback. Overall, the adoption of 3D printed aluminum in healthcare signifies a transformative step toward improved patient outcomes and operational efficiencies.
Challenges in 3D Printing Aluminum
3D printing aluminum presents several challenges that can impact production quality and material performance.
Material Properties
Aluminum’s thermal conductivity poses a significant challenge. High thermal conductivity causes rapid cooling during the printing process, increasing the likelihood of warping. Reduced ductility can also occur, resulting in brittleness in printed parts. Additionally, aluminum’s susceptibility to oxidation complicates the handling requirements during printing. This material must undergo proper surface treatments to maintain its desired properties. Variability in grain structure can lead to inconsistent mechanical properties, requiring thorough quality testing. Overall, the intricacies of aluminum behavior during additive manufacturing demand careful consideration to ensure part reliability.
Technical Limitations
Technical limitations hinder the efficiency of 3D printing aluminum. Print speed remains a concern, as slower build rates can introduce delays in production schedules. Some additive manufacturing technologies struggle to achieve the high temperatures necessary for optimal layer fusion, affecting density and integrity. Equipment costs also present barriers, requiring investment in specialized machines capable of handling aluminum’s unique properties. These machines may necessitate ongoing maintenance and calibration to function correctly. While techniques like Selective Laser Melting improve quality, they still face challenges in handling complex geometries effectively. Addressing these limitations is critical for advancing aluminum 3D printing applications.
Future Trends in 3D Printing Aluminum
Emerging trends in 3D printing aluminum signal a shift towards enhanced capabilities and wider applications. Innovations in materials science are leading to aluminum alloys specifically designed for additive manufacturing, improving the mechanical properties of printed parts.
Increased focus on automation is optimizing the 3D printing process, resulting in higher efficiency and reduced production times. Advanced software tools streamline print preparation, allowing for complex geometries and designs that traditional methods struggle to achieve.
Integration of artificial intelligence in the design and printing stages is revolutionizing predictive maintenance and quality control. These AI systems analyze data to improve reliability, leading to fewer defects and better performance in end-use parts.
Sustainability continues to gain importance. Secondary aluminum usage in 3D printing minimizes environmental impact, promoting resource recycling and aligning with industry goals for waste reduction. This approach not only lowers costs but also enhances the appeal of aluminum as a sustainable choice.
Collaborative efforts among industries are also shaping the future. Research partnerships between manufacturers and academic institutions foster advancements in techniques like Laser Powder Bed Fusion and Direct Energy Deposition, paving the way for more efficient production processes.
Potential growth in the medical field indicates a promising future. Custom medical devices and implants made through aluminum 3D printing may enhance patient outcomes while streamlining production timelines. Increased demand for personalized solutions in healthcare drives this trend.
Overall, rapid advancements in 3D printing aluminum continue to redefine manufacturing. As technology evolves, so do its applications, expanding capabilities across industries.
3D printing aluminum is revolutionizing manufacturing by offering innovative solutions that enhance efficiency and sustainability. Its lightweight and durable properties make it an ideal choice for industries like aerospace and automotive. As technology advances the capabilities of additive manufacturing, the potential for complex designs and rapid prototyping grows.
While challenges such as material properties and technical limitations remain, ongoing research and development are paving the way for improved applications. The future looks bright for 3D printed aluminum as it continues to meet modern demands for flexibility and performance. With a focus on sustainability and efficiency, this technology is set to play a vital role in shaping the future of various sectors.





